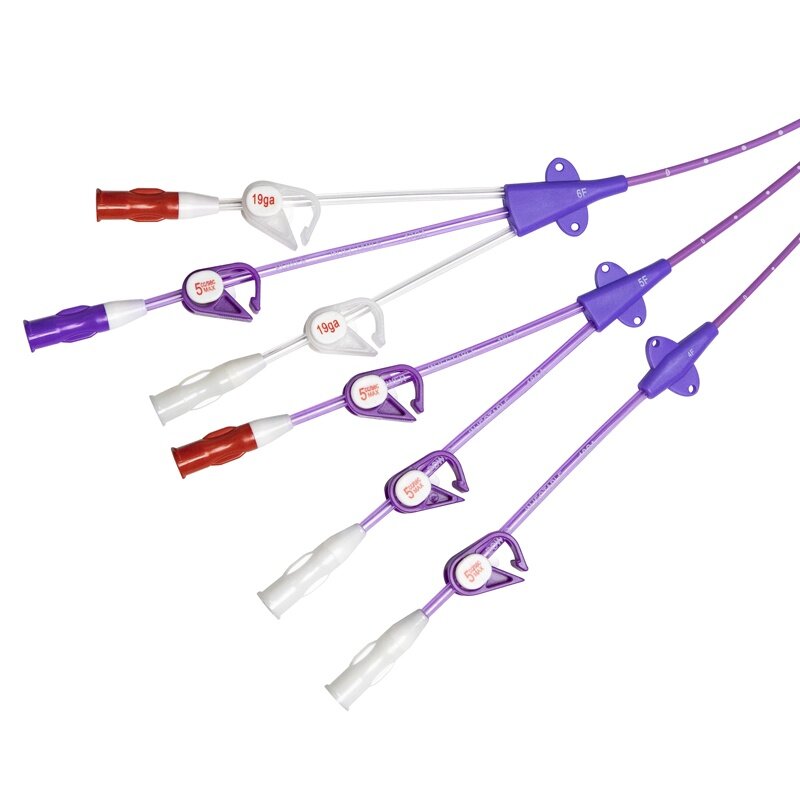
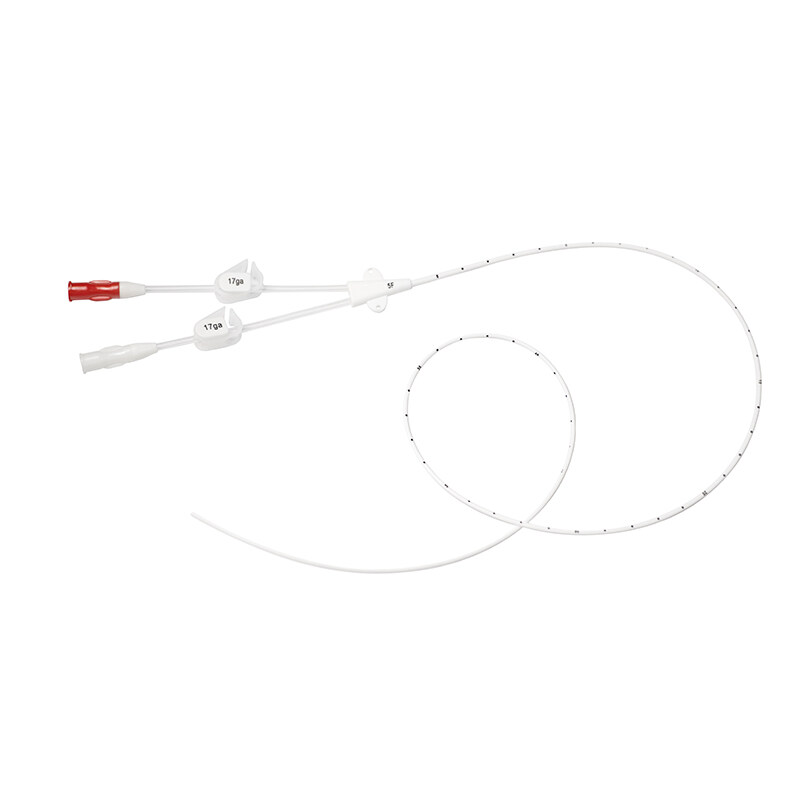
In pediatric clinical nursing, the establishment and maintenance of venous access have always been a major challenge for healthcare providers. Children have thin blood vessels and low compliance. Long-term infusion not only requires repeated punctures but also may lead to complications such as phlebitis due to drug irritation. Recently, Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology successfully inserted a midline catheter into a 6-year-old child. Through standardized nursing, the catheter was safely indwelled for 17 days without complications, providing a high-quality solution for short-to-medium-term intravenous therapy in pediatrics. Today, starting from this case, we will analyze the unique advantages and core nursing techniques of midline catheters in pediatrics.
1.Case Review: 17 Days from Emergency Treatment to Smooth Recovery
Patient Condition :
A 6-year-and-11-month-old female child suffered pancreatic injury due to abdominal trauma and required intravenous infusion of parenteral nutrition and symptomatic drugs (osmotic pressure < 900mOsm/L). Traditional indwelling needles were prone to failure due to drug irritation, while central venous catheters (such as CVC) posed a high risk of vascular injury to young children. After assessment, the medical team decided to use a midline catheter for treatment.
Treatment Process
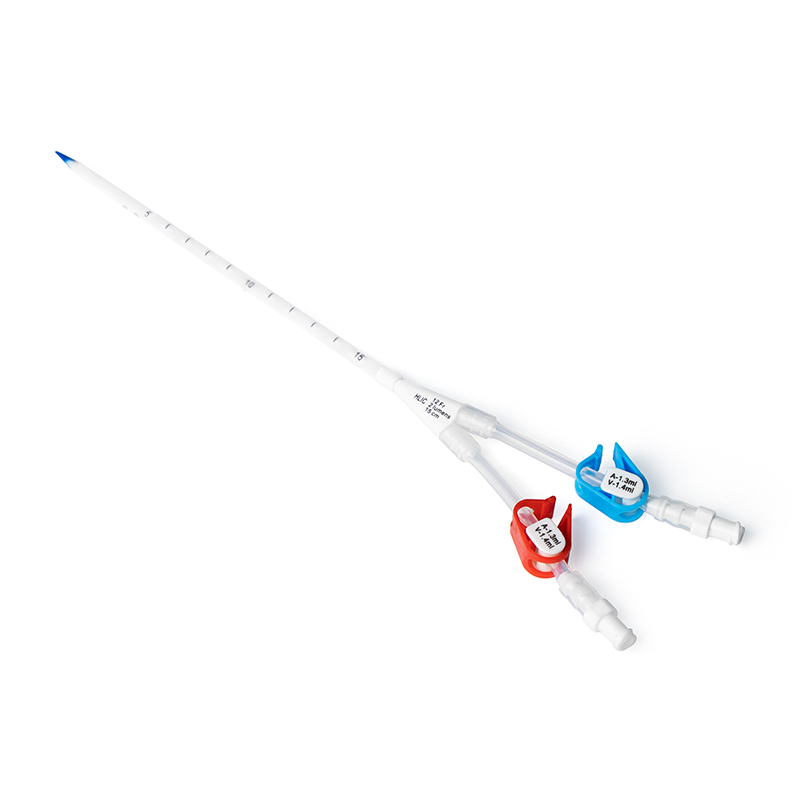
Catheterization Site Selection: Based on the child's vascular conditions, the basilic vein of the left upper arm was selected for midline catheter insertion, ensuring that the catheter tip did not exceed the axilla.
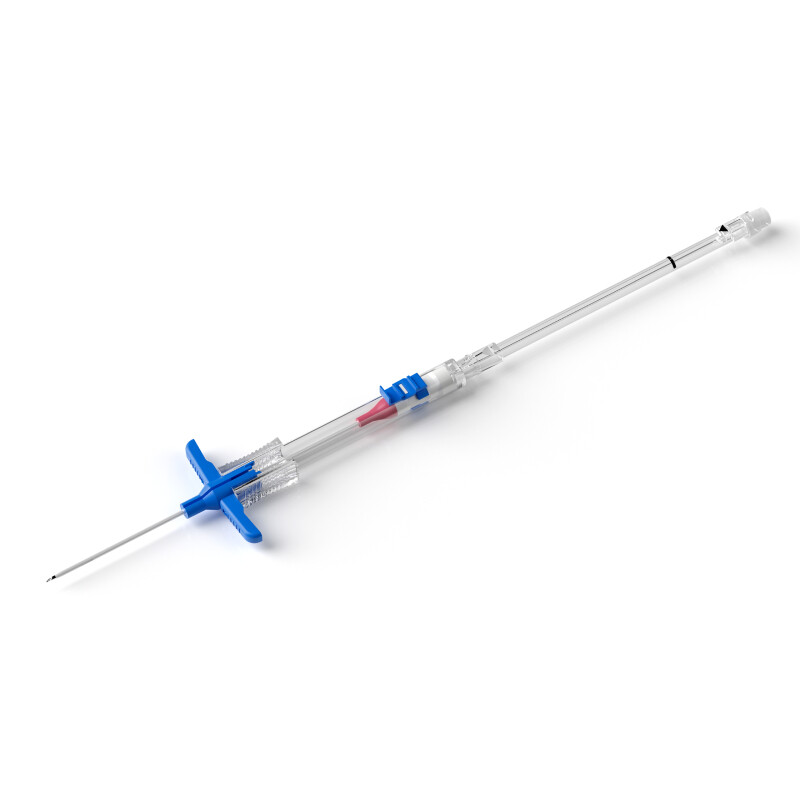
Key Operation Points: The catheter was inserted under ultrasound guidance using the modified Seldinger technique. Throughout the process, psychological nursing was provided (playing animations and offering lollipops), and the child showed good compliance.
Nursing Outcome: During the 17-day indwelling period of the catheter, there were no complications such as phlebitis, infection, or occlusion. The parenteral nutrition therapy was successfully completed, and the child was discharged after recovery upon catheter removal.
2.Three Core Advantages of Midline Catheters for Children
Compared with traditional venous access devices, midline catheters show significant advantages in pediatric patients, especially suitable for short-to-medium-term treatment needs (5-14 days):
(1)Reducing Pain and Trauma, Improving Pediatric Compliance
Children's blood vessels are thin and fragile. Traditional indwelling needles need to be replaced every 2-3 days, and repeated punctures not only increase the child's pain but also may cause vascular damage. A midline catheter can be indwelled for up to 4 weeks, reducing the number of punctures by more than 70%. In this case, the child completed the entire course of treatment with a single catheterization, avoiding the fear of multiple punctures and significantly improving compliance during the nursing process.
(2)Lowering the Risk of Complications, Adapting to Pediatric Treatment Needs - Wider Drug Compatibility:
Midline catheters can safely infuse parenteral nutrition, antibiotics, and other low-to-moderate irritating drugs, solving the problem of phlebitis caused by high osmotic pressure drugs (e.g., > 600mOsm/L) in traditional peripheral catheters.
(3)Low Infection Risk: The catheter tip is located in the upper arm vein (not exceeding the axilla), far from the central vein. Moreover, it is made of polyurethane, which has good biocompatibility. No infection occurred during the 17-day indwelling period in this case, confirming its safety.
(4)Convenient and Flexible Operation, Adapting to Children's Activity Needs
Midline catheters can be inserted at the bedside by nurses under ultrasound guidance, which is convenient and fast. After the catheter is fixed, it does not affect the child's limb movement, and daily activities such as bathing and playing are not restricted, significantly improving the child's quality of life.
3.Key Techniques for Insertion and Maintenance of Pediatric Midline Catheters
Based on case experience and clinical standards, the successful application of pediatric midline catheters requires mastering the following operation points:
Pre-Insertion: Accurate Assessment + Personalized Preparation
Vascular Assessment: Priority is given to selecting the non-dominant upper limb vein. Ultrasound is used to confirm that the vessel diameter is ≥ 2mm, avoid venous valves, and stay away from joint flexion areas.
Psychological Intervention: To address children's fear, animations are used to distract attention before the operation, comforting toys are provided, and local anesthesia is used if necessary to improve the success rate of puncture.
Intra-Insertion: Standardized Operation + Fine Fixation
Technique Selection: Due to the thin blood vessels of children, the modified Seldinger technique under ultrasound guidance is recommended to reduce vascular damage.
Fixation Techniques: The catheter is fixed using a "special catheter fixation device + tension-free adhesion + elevated platform method" to prevent displacement caused by the child's activities. The puncture site is covered with a sterile transparent dressing, and the insertion date is marked for easy observation.
Post-Insertion: Scientific Maintenance + Dynamic Monitoring
Standard Flushing and Locking: Use 10ml normal saline for pulsatile flushing of the catheter, and perform positive-pressure locking after the end of infusion to avoid blood reflux and occlusion.
Complication Monitoring: Evaluate the puncture site daily for redness, swelling, or exudation, and measure changes in arm circumference (an increase of > 2cm requires vigilance for thrombosis). A phlebitis grading scale (Grade 0-4) is used for dynamic monitoring to detect and manage abnormalities early.
Parental Education: Instruct parents to prevent the child from scratching the catheter and keep the dressing dry. Advise them to report immediately if complications such as catheter dislodgement or puncture site bleeding occur.
4.Clinical Implications: Promotional Value of Midline Catheters in Pediatrics
This case verifies the safety and effectiveness of midline catheters in short-to-medium-term intravenous therapy for children. Compared with PICC, midline catheters are easier to operate and cost less; compared with traditional intravenous indwelling needles, they have a longer indwelling time and fewer complications, which can significantly reduce the nursing burden. In the future, with the continuous advancement of technology, midline catheters are expected to become the preferred tool for pediatric intravenous therapy, providing a safer and more comfortable infusion experience for pediatric patients. Haolang Medical will also continue to pay attention to the needs of pediatric vascular access, launch midline catheters and nursing kits more suitable for children, and contribute to the improvement of clinical nursing quality.
Case Source: Zhou, Y. F., & Zhang, H. M. (2025). Nursing care of a child with a midline catheter inserted [J]. General Nursing, 23(13), 2592-2594.